9 Scientific Benefits of Following Plant-Based Diet
In recent years, a surge in the adoption of a plant-based diet has been witnessed globally. The shift isn't merely a fashionable trend; it's underpinned by substantial scientific evidence.
Adopting a diet predominantly based on plants isn't only a testament to ethical choices or sustainability but also a tribute to one's health. From the intricacies of our cellular health to the holistic functioning of our body, a plant-based diet touches upon every aspect of our well-being.
In the subsequent sections, we will embark on a detailed journey through nine science-backed advantages of such a healthy plant-based eating dietary regimen.
1. Natural Weight Management and Reduced Obesity Risk
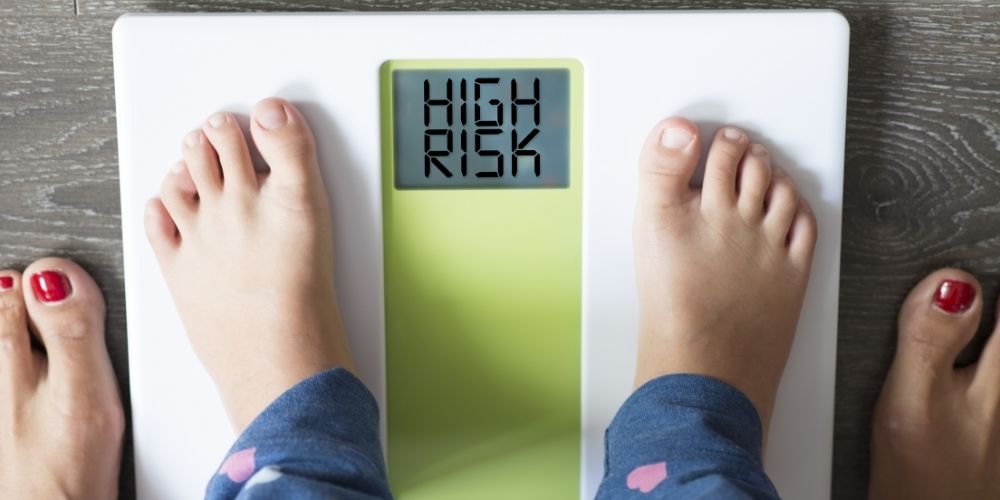

The obesity epidemic plagues numerous nations with its adverse health implications and increased mortality rates. Interestingly, a plant-based diet emerges as a potent solution:
High Fiber Content: Plants are incredibly fiber-rich, unlike processed foods and meat. This ensures prolonged feelings of satiety, preventing overeating and unnecessary calorie intake.
Lower Caloric Density: Vegetables and fruits, being high in water content, provide essential nutrients without excessive calories. This means you can consume more, stay full, and manage weight.
Reduced Saturated and Trans Fats: These fats, commonly found in animal products and processed foods, are culprits behind weight gain. A plant-centric diet significantly reduces their intake.
2. Decreased Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases
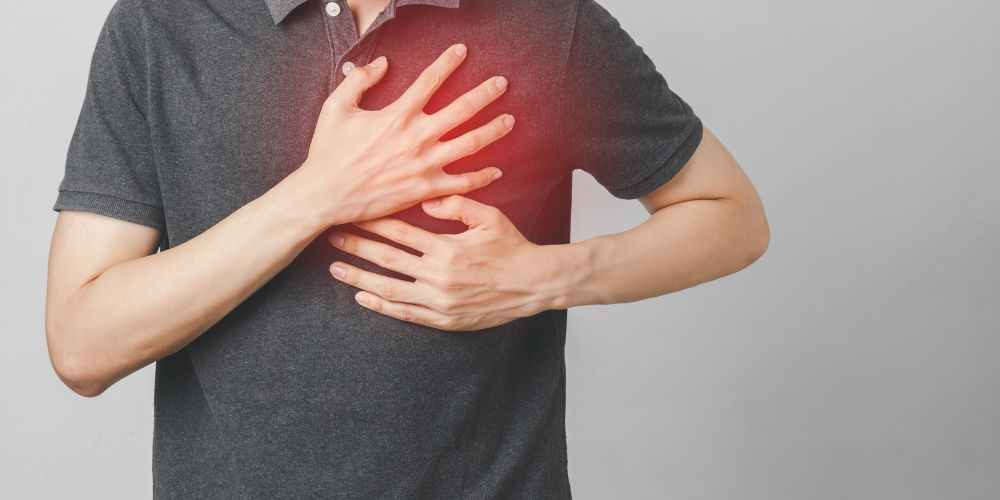

Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death worldwide. However, plant-based diets can significantly mitigate this risk:
Cholesterol: Animal products are primary cholesterol sources. By limiting their intake, one directly reduces bad cholesterol levels. Plant-based diets introduce beneficial compounds that help remove cholesterol from blood vessels.
Blood Pressure: Rich in potassium, plant foods help dilate blood vessels, facilitating smoother blood flow and reducing blood pressure.
Phytonutrients: Found exclusively in plants, phytonutrients like flavonoids protect the heart by reducing inflammation and preventing arterial plaque formation. You can also use plant based protein powder for enhanced well-being.
3. Enhanced Digestive Health
Digestive health, often overlooked, is paramount for overall well-being. A plant-based diet offers:
Digestive Enzymes: Certain fruits like pineapples and papayas contain enzymes that assist in breaking down food and improving digestion.
Gut Microbiota: Fiber from plants acts as a prebiotic, nourishing beneficial gut bacteria. A balanced gut microbiome is linked to reduced risks of digestive disorders, improved immunity, and even better mental health.
Detoxification: Leafy greens and cruciferous vegetables aid the liver in its detoxification processes, ensuring toxins are efficiently eliminated3. Reduces the Risk of Certain Cancers
Cancer is a complex disease, but dietary choices can influence its risk. Vegan diet offers:
Antioxidants: These compounds combat free radicals, which can cause cellular damage.
Phytochemicals: These chemicals are found in plants and protect against certain cancers.
Lower Meat Consumption: Some processed meats have been linked to cancers like colon cancer. A plant-based diet naturally reduces this risk.
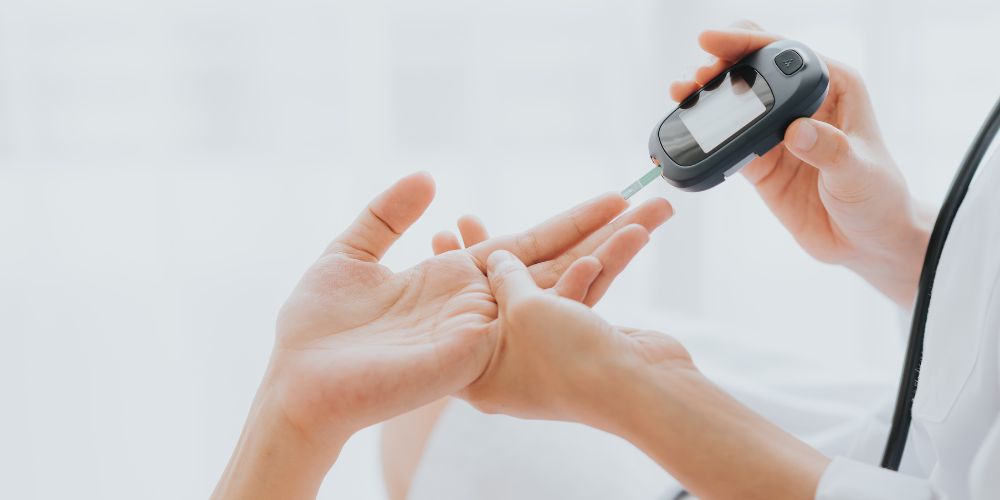
4. Lower Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
The prevalence of Type 2 diabetes has skyrocketed in modern societies, largely influenced by dietary patterns and sedentary lifestyles. Turning to plant based products presents promising solutions:
Glycemic Index: Most plant-based foods have a low glycemic index. This means that they release sugar slowly into the bloodstream, aiding in the stable regulation of blood sugar levels.
Insulin Sensitivity: The fiber-rich quality of plant foods aids in the improvement of insulin sensitivity. When the body responds better to insulin, it's less likely to convert sugar into stored fat.
Magnesium: Abundant in leafy greens, legumes, and whole grains, magnesium plays a crucial role in glucose metabolism, ensuring our body's efficient utilization of sugar.
5. Protection Against Certain Cancers
Cancer, a multifaceted disease, has several risk factors. Diet significantly influences these risks, and plant-based diets show protective qualities:
Antioxidants: Bright-colored fruits and vegetables are laden with antioxidants. These compounds combat free radicals that can damage cellular structures, including DNA, thus reducing cancer risks.
Fiber: Besides digestive health, fiber aids in eliminating potential carcinogens from our system, which is particularly vital in preventing colorectal cancers.
Phytochemicals: Plants contain compounds such as isoflavones and polyphenols, which have been shown to inhibit tumor growth and reduce inflammation.
6. Bone Health Improvement
Bone health is foundational for mobility and the overall structural integrity of the body. Plant-based diets offer essential nutrients that ensure strong bones:
Calcium Sources: Contrary to popular belief, dairy isn't the only source of calcium. Leafy greens, fortified plant milk, almonds, and tofu are excellent calcium sources.
Vitamin K: Abundant in green leafy vegetables, it plays a pivotal role in bone mineralization and preventing osteoporosis.
Anti-acidic Nature: Most plant foods are alkaline or neutral, which means they don't leach calcium from bones, unlike some animal-based acidic foods.
7. Boosted Mental Well-being
Mental health and diet share a profound connection. Several components of a plant-based diet directly enhance cognitive function and mood:
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: While fish is a well-known source, flaxseeds, walnuts, and chia seeds are plant-based sources of these essential fatty acids that boost brain health.
Vitamin B-complex: Crucial for brain function, B vitamins are abundant in whole grains, beans, peas, and nuts. You are most likely to find them in a plant based sleep aid.
Tryptophan: Found in seeds, nuts, and certain fruits, it's a precursor for serotonin, the "feel-good" neurotransmitter.
8. Healthy Skin and Improved Complexion
Skin, our body's largest organ, reflects our internal health. A plant-based diet can be the secret to radiant skin:
Hydration: Fruits like watermelon, cucumber, and oranges have a high water content, ensuring our skin stays hydrated and supple.
Vitamins C & E: Both are potent antioxidants. While Vitamin C boosts collagen production, Vitamin E protects skin from oxidative damage and inflammation.
Beta-carotene: Found in carrots, sweet potatoes, and bell peppers, it protects the skin from sun damage and supports repair.
9. Increased Longevity and Better Quality of Life
Humanity's pursuit for ages has been the promise of a longer, more fulfilling life. A plant-based diet can be a step closer:
Lowered Disease Risk: As we've explored, plant-based diets reduce risks for several major diseases, promising not just longer but healthier lives.
Nutrient Density: Consuming nutrient-rich foods ensures optimal cellular function, slowing aging and boosting vitality.
Detoxification: Regular consumption of plant foods aids the body in flushing out toxins, ensuring internal cleanliness and long-term health.
FAQs:
Conclusion
The evidence is compelling. A plant-based diet isn't a mere dietary preference but a conscious choice for holistic well-being. From cellular health to environmental impact, the ripple effects of this choice are expansive. With every meal, individuals have the power to define their health trajectory and play a part in global sustainability.
The science speaks volumes, but the true testament lies in the lived experiences of millions who have witnessed transformative changes by embracing plants. As we move forward, it's clear that the path to longevity, vibrant health, and a sustainable planet intertwines with the foods we choose to consume.
Are you looking for plant-based options? CKE Naturals has everything for you!




